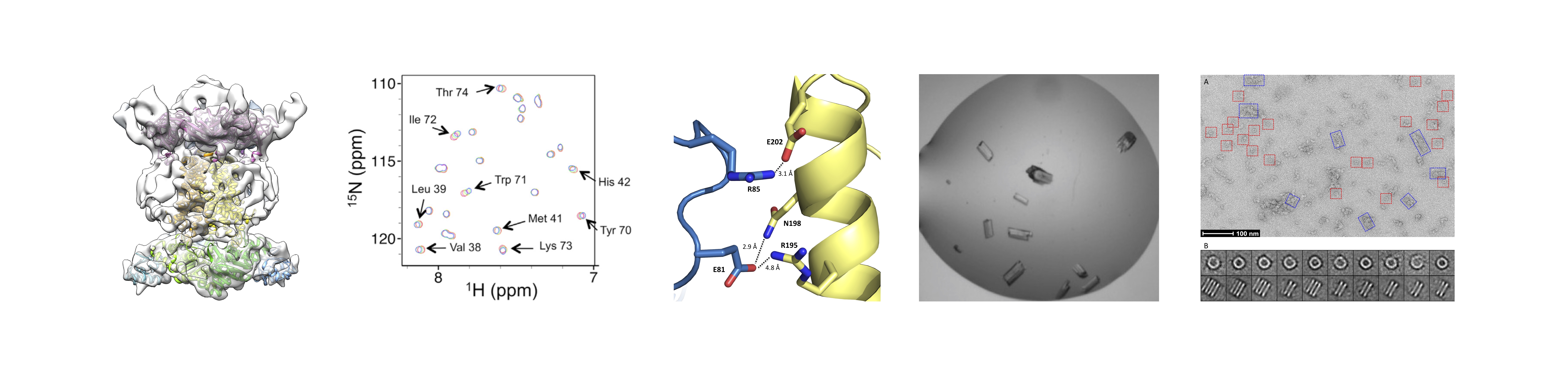
Protein nano-machines are large macromolecular assemblies that perform a mechanical function, such as rotation (bacterial flagellum, ATP synthase), extension/contraction (cytoskeleton elements, pili) or macromolecular transport (protein secretion systems).
We use structural methods (cryo-EM, NMR spectroscopy, X-ray crystallography, modeling etc...) combined with biophysical techniques to decipher the structure of these assemblies. Our goal is to exploit this information to understand their mechanism of action, and their assembly.
Ultimately, this could be used for the design of nanotechnology devices, as well as for developing new drugs.